You have /5 articles left.
Sign up for a free account or log in.

Istockphoto.com/kali9
College leaders and policy makers are paying more attention to the millions of adults in the U.S. who attended college but didn’t earn a credential. Yet many questions remain about this population -- not just how to better recruit and serve them, but who they are.
A newly released report from the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center helps fill in some of the blanks.
The nonprofit group used data from institutions that collectively account for 97 percent of the nation’s postsecondary enrollments. It was able to track individual students across institutional boundaries, including when they left college and if they later enrolled at another institution.
The result is an unusually extensive view of the “educational trajectories” of the 36 million Americans the center identified who left college without receiving a degree or certificate. Several experts said the findings have wide implications for colleges, systems and federal and state policy makers.
As of December 2018, 36 million people from the center’s database had attended college since 1993 but failed to earn a credential at any U.S. institution and were no longer enrolled in college. That figure was up 6.6 million, or 22 percent, during the five years since the center first released a data report on this population.
The center was able to make some conclusions about who these former students tend to be. Its findings included:
- Most are nearing middle age, with a median of age of 39 and an average age of 42.
- 56 percent left postsecondary education when they were in their 20s or younger.
- 51 percent are women.
- The typical American with some college, no degree left postsecondary education a decade ago.
- These people had a short college career (53 percent left within two years).
- Most attended one institution (74 percent).
- Community colleges were the starting and last-enrolled institution for two-thirds (67 percent).
Finding Likely Completers
A growing number of colleges and organizations are seeking to find these students to encourage them to return to college and earn a credential, in part so they didn’t spend time and rack up debt without getting a payoff in the job market.
Perhaps most notably, the Institute for Higher Education Policy’s ongoing three-year initiative, dubbed Degrees When Due, helps colleges and states identify former students who earned college credits but didn’t complete.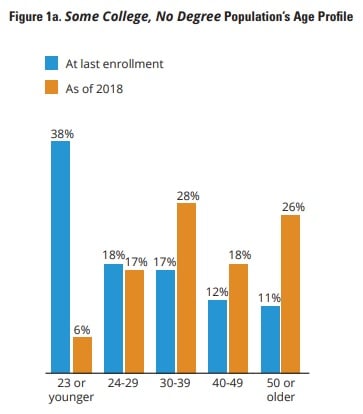
The center’s new data show that roughly 10 percent of people with some college, no degree have a high potential to earn a credential if they re-enroll. These 3.5 million “potential completers” carry the equivalent of at least two years’ worth of full-time college enrollment during the past decade.
“These students are the most likely to return and finish college,” the center said.
Potential completers are younger than the rest of their peers with some college, no degree. Most (58 percent) are below age 30, compared to 23 percent over all. They also were more likely to have been in their 20s when they last attended college (75 percent compared to 56 percent) and were enrolled more recently.
This group tends to weave in and out of college more frequently than the overall population studied in the report. The center found that 64 percent of potential completers stopped out of college more than once, compared to 40 percent of the broader population.
During the five years since the last center report on this group, potential completers were far more likely to have returned to postsecondary education (24 percent compared to 9 percent) and to have earned a credential (33 percent of re-enrolling potential completers compared to 23 percent of those with only a single term of prior enrollment, and 22 percent of those with multiterm enrollments of less than the equivalent of two years).
“Potential completers are the most relevant sub-group for institutions looking to increase enrollments today, as well as for policymakers looking to reach state and national postsecondary attainment goals tomorrow,” the report said.
Success Among the Re-enrolled
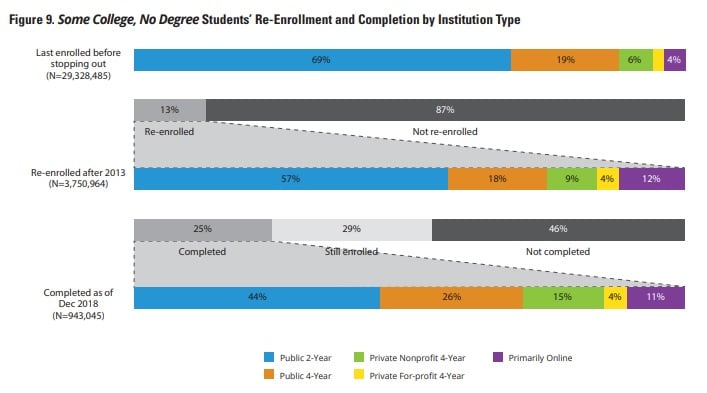
Roughly a million former college students without a credential whom the center identified in its 2013 report have since re-enrolled and are now completers.
These 940,000 credential holders comprise 25 percent of the 3.8 million people with some college, no degree who re-enrolled sometime in the past five years, the center found. Another 1.1 million re-enrolling students were still in college without a credential as of December 2018.
That means 54 percent of returning students with some college, no degree have earned or are still on the path toward a credential.
This group represents a windfall for higher education, and for society, said Doug Shapiro, the center’s executive director.
“This is a population that’s been written off,” he said in an interview. “Imagine what we could do as a nation if we really focused on these students.”
Two common characteristics about re-enrolling completers stood out to Shapiro and other experts:
- They were more likely to re-enroll and complete at a different institution than the one they last attended, but in the same state. Only 38 percent returned to the same institution.
- Online enrollees were more likely to have returned to online institutions. And although the center does not name individual colleges in its publicly released reports, it said large, national online institutions were overrepresented among re-enrolling students and completers.
Courtney Brown, vice president of strategy impact at the Lumina Foundation, said it’s probably not surprising that re-enrolling students tend to prefer a different institution when they return to college.
“They got burned” the first time around, she said.
Brown said the center’s new data include a “glimmer of hope” about achievement gaps for students from underrepresented minority groups.
Among the 940,000 “new completers,” the center found that African Americans and Hispanics were overrepresented among earners of bachelor’s and associate degrees. They made up 25 percent of bachelor’s degree earners in this group, compared to 16 percent in the center’s national sample of college graduates, and 32 percent of associate degree earners, compared to 23 percent over all.
Even so, Brown said the report’s finding that 36 million Americans attended college but didn’t earn a credential is a sobering reminder of the magnitude of the challenge.
“We’re failing our first-time students at an alarming rate,” she said.